Antibody fragments are used as substitutes to conventional monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) in diagnostic and therapeutic applications, among which scFvs are one of the most popular types. scFvs can be produced in various expression systems and modified into plenty of different Ab formats. As they can be expressed in bacteria (e.g., Escherichia coli), scFvs are smaller and therefore easier and less expensive to manufacture, whereas mAbs typically need a mammalian expression system. Moreover, the size of scFvs still offers benefits in clinical research, including reduced immunogenicity when administered in vivo for the absence of an Fc region; better tissue penetration, which is useful for therapeutic and imaging applications; and rapid blood clearance, which is useful for imaging applications.
Complete antigen binding sites are included in scFvs, such as the variable heavy (VH) and variable light (VL) domains, of an Ab. Through the introduction of a flexible peptide linker (e.g., (GGGGS)3), the VH structural domain is linked to the VL structural domain. Alternative monovalent fragments to scFv include dsFv that constitutes VH and VL chains connected by disulfide bonds inserted into the frame region. dsFvs have a higher degree of stability and do not aggregate in comparison to scFvs.
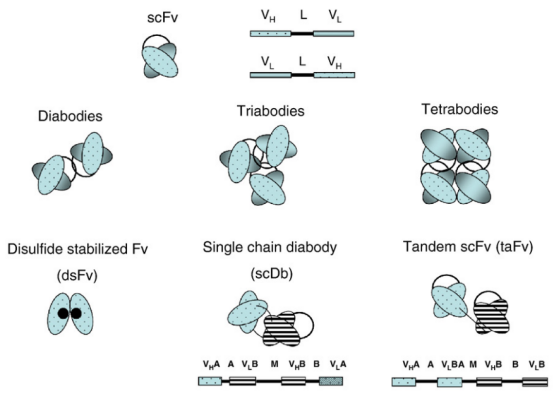
Fig 1 . Structure of scFv and derivatives
scFv Fragment for Therapeutic Use
After years of discovery and engineering, scFv and scFv-based fragments have emerged as viable therapeutic and diagnostic alternatives to mAbs for cancer, autoimmune diseases, inflammation, chronic viral diseases, etc. Several scFv fragments have been approved for therapeutic use, such as Blinatumomab (Blincyto), Moxetumomab pasudotox (Lumoxiti), Brolucizumab (Beovu), and Tebentafusp (Kimmtrak).
Moxetumomab pasudotox
Moxetumomab pasudotox (Lumoxiti) is a CD22-targeting cytotoxin. It comprised of a recombinant, murine immunoglobulin variable domain fused to a truncated Pseudomonas exotoxin, PE38, that inhibits protein synthesis. Moxetumomab pasudotox has a molecular weight of approximately 63 kDa and is produced by recombinant DNA technology in E. coli. It was developed by Medimmune (R&D arm of AstraZeneca) and approved for treating adult patients with relapsed or refractory hairy cell leukemia (HCL).
Brolucizumab
Brolucizumab was developed by Novartis to treat patients with exudative (wet) age-related macular degeneration (AMD), diabetic macular oedema, and macular oedema secondary to retinal vein occlusion. Brolucizumab is an E. coli-produced humanized scFv antibody fragment that targets human vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) with a molecular weight of around 26 kDa.
Tebentafusp (Kimmtrak)
As a bispecific gp100 peptide-HLA-directed T cell receptor CD3 T cell engager, Tebentafusp (Kimmtrak) is indicated for treating HLA-A*02:01-positive adult patients with unresectable or metastatic uveal melanoma. Tebentafusp was developed by Immunocore and produced in E. coli cells with 77 kDa molecular weight.
Yaohai Bio-Pharma Offers One-Stop CDMO Solution for Antibody Fragments
scFv Fragment Pipelines
|
Generic Name
|
Brand Name/ Alternative Name
|
Target
|
Expression System
|
Indications
|
Manufacturer
|
R&D Stage
|
|
Blinatumomab
|
BiTE-MT-103, bscCD19xCD3, AMG-103, MEDI-538, ビーリンサイト, Blincyto, 倍利妥
|
CD19, CD3
|
CHO cell
|
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), lymphoma
|
Amgen, BeiGene
|
Approval
|
|
Brolucizumab-dbll
|
AL-86810, XSZ53G39H5 (UNII code), RTH-258, ESBA-1008, DLX-1008, Beovu, ベオビュ
|
VEGF-A
|
Escherichia coli (E. coli)
|
Macular degeneration
|
Novartis
|
Approval
|
|
Moxetumomab pasudotox
|
Lumoxiti, scFv-PE38
|
CD22
|
E. coli
|
Hairy cell leukemia
|
AstraZeneca,Innate
|
Approval
|
|
Tebentafusp
|
Kimmtrak, CD3, gp100
|
CD3, gp100
|
E. coli
|
Unresectable or metastatic uveal melanoma
|
Immunocore
|
Approval
|
|
Licaminlimab
|
ESBA-1622, LME-636, OCS 02, ESBA 1622
|
TNF-α
|
Pending update
|
xerophthalmiaAnterior uveitis
|
Novartis Pharma AG、Oculis SA、Alcon AG
|
Phase II
|
|
SAR-443726
|
anti-IL13/OX40L nanobody (Sanofi)
|
IL13R, OX40L
|
Pending update
|
Genetic diseases and malformationsSkin and musculoskeletal disorders
|
Sanofi
|
Phase I
|
|
Deoxymab
|
3E10, PAT-DX1
|
DNA
|
Pending update
|
Pancreatic cancer,Systemic lupus erythematosus
|
Patrys Ltd.
|
Phase I
|
|
VTx 002
|
Pending update
|
TDP43
|
Pending update
|
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
|
VectorY BV
|
Pre-clinical
|
|
VH-7Vk9
|
TDP-43 targeting single chain antibody, VH-7Vk9
|
TDP43
|
Pending update
|
Frontotemporal dementia
|
ImStar Therapeutics, Inc.
|
Pre-clinical
|
|
scFv-h3D6
|
bapineuzumab derivative, scFv-h3D6
|
APP
|
Pending update
|
Alzheimer's Disease
|
Universitat Autonoma de Barcelona
|
Pre-clinical
|
|
Fv-Hsp70
|
RBB-001, Fv-Hsp72
|
DNA, HSP70
|
Pending update
|
Ischemic stroke
|
Rubicon
|
Pre-clinical
|
|
SMET-D1
|
Pending update
|
Pending update
|
Pending update
|
Arthritis, eczema, psoriasis
|
CentryMed
|
Pre-clinical
|
|
PMC-401s
|
Anti-ANG2 antagonistic fully human ScFv, PMC-401s
|
Ang2
|
Pending update
|
Diabetic retinopathy, Macular degeneration
|
PharmAbcine Inc.
|
Pre-clinical
|
|
T-1649
|
Pending update
|
TNF-α
|
Pending update
|
Psoriasis
|
Teraclon
|
Pre-clinical
|
|
IMX-120
|
GLUT-1 antibody scFv-containing nanoparticles
|
GLUT1
|
Pending update
|
Ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, osteoarthritis
|
Immix Biopharma, Inc.
|
Pre-clinical
|
|
CGX-208
|
anti-misfolded alpha-synuclein scFv
|
α-synuclein
|
Pending update
|
Parkinson's disease
|
Cognyxx Pharmaceuticals
|
Pre-clinical
|
|
GTB-5550
|
GTB-5550 TriKE, GTB-5550
|
CD276
|
Pending update
|
Squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck, Multiple myeloma
|
GT Biopharma
|
Pre-clinical
|
|
scFv-235
|
single chain variable antibody fragment, scFv-235
|
TAU
|
Pending update
|
Alzheimer's Disease
|
Lundbeck Foundation
|
Pre-clinical
|
|
TA-101
|
recombinant single domain antibody fragment, TA-101
|
TNF-α
|
Pending update
|
Rheumatoid arthritis
|
TechnoPhage
|
Pre-clinical
|
|
DNX-214
|
Pending update
|
Pending update
|
Pending update
|
Wet age-related macular degeneration
|
DNX
|
Pre-clinical
|
|
NI-205
|
Pending update
|
TDP43
|
Pending update
|
Frontotemporal dementia
|
Biogen, Neurimmune
|
Pre-clinical
|
|
ARA-8
|
Pending update
|
Pending update
|
Pending update
|
Inflammation
|
|
Pre-clinical
|
|
P-1000
|
Pending update
|
Pending update
|
Pending update
|
Cancer
|
German Cancer Research Center
|
Pre-clinical
|
|
MRT-201
|
granzyme B synthetic antibody, GranzymeB-Fc-scFv4D5, MRT-201
|
HER2
|
Pending update
|
Cancer
|
Clayton、Mirata
|
Pre-clinical
|
|
MRT-101
|
Granzyme B/antibody fusion protein, GrB-Fc-IT4
|
TWEAK
|
Pending update
|
Cancer
|
Clayton、Mirata
|
Pre-clinical
|
Reference:
[1] Weisser NE, Hall JC. Applications of single-chain variable fragment antibodies in therapeutics and diagnostics. Biotechnol Adv. 2009 Jul-Aug;27(4):502-20. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2009.04.004.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 SL
SL
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 ET
ET
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 AF
AF
 MS
MS
 BE
BE
 MK
MK
 UR
UR
 BN
BN