Minicircle DNA (mcDNA) is a smaller non-viral DNA vector derived from a parental plasmid DNA-like structure. Minicircle DNA differs from conventional plasmid DNA in that it contains promotor and gene of interest (GOI), without origin of replication (ORI) and selection marker (selMark). Minicircle DNA is produced in bacteria through in vivo recombination to remove extra sequences (called mini-plasmid) from plasmid DNA. Due to its safety, minicircle DNA has gained popularity as a non-viral vector for gene therapy, DNA vaccines, etc.
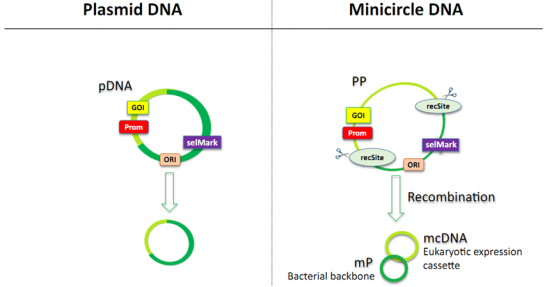
Figure 1. Structure of Plasmid DNA (pDNA) and Minicircle DNA (mcDNA)
Minicircle DNA Recombination Systems
There are four main minicircle DNA in vivo recombination systems that have been studied, including Phage λ integrase, Phage P1 Cre recombinase, ParA resolvase, PhiC31 integra se/I-SceI.
|
Strategy
|
Phage λ integrase
|
Phage P1 Cre recombinase
|
ParA resolvase
|
PhiC31 integra se/I-SceI
|
|
Mechanism
|
Tyrosine recombinase, which functions through proteins FIS and IHF to catalyze the recombination of att hybrid sites
|
Site-specific tyrosine recombinase, which performs a bidirectional recombination when binding to loxP sites
|
Serine recombinase, which performs an irreversible and unidirectional recombination between two identical MRSsites
|
Serine recombinase, which mediates unidirectional recombination between attP/attB binding sites, while I-SceI endonuclease cleaves the product-related impurities and unrecombined parental plasmid
|
|
Features
|
Depend on the expression of host factors FIS and IHF; intrinsic toxicity; Residual parental plasmid and mini-plasmid
|
Residual parental plasmid and mini-plasmid
|
High yield; Residual parental plasmid and mini-plasmid
|
Degradation of parental plasmid associated reduced yield
|
Yaohai Bio-Pharma Offers One-Stop CDMO Solution for Minicircle DNA
Reference:
[1] Almeida AM, Queiroz JA, Sousa F, Sousa Â. Minicircle DNA: The Future for DNA-Based Vectors? Trends Biotechnol. 2020 Oct;38(10):1047-1051. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2020.04.008.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 SL
SL
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 ET
ET
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 AF
AF
 MS
MS
 BE
BE
 MK
MK
 UR
UR
 BN
BN