Characterization of Heavy Chain Antibodies
In the three million years that have passed since the split of the New World and Old World Camelidae, heavy chain-only antibodies have developed from the traditional immunoglobulin loci and carry certain structural changes that have been preserved in all camelid species.
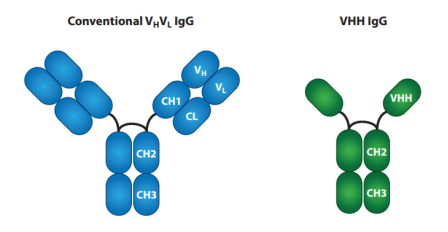
Fig 1. Structure of heavy chain-only antibodies
Biophysical Properties of Nano-antibody
Nano-antibody (Nb), also called single domain antibody (sdAb) or heavy-chain variable (VHH), derived from camelid heavy chain antibodies, is the minimum known native antigen-specific binding functional fragment, with a molecule weight of only ~15 kDa. Nbs are highly stable, durable, and soluble. Additionally, because of their small size, Nbs can bind epitopes that full-size antibodies cannot reach and pass through narrow cavities.
With a preserved disulfide bond between Cys23 and Cys94, VHHs have a normal IgV fold with nine β strands. Three hypervariable loops joined by four conserved framework sections make up the V domain, just like in conventional IgGs.
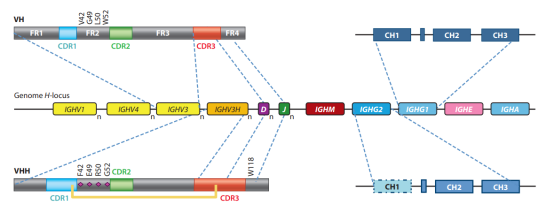
Fig 2. Sequence Feature of single-domain antibody (sdAb)
Applications of Nano-antibody
There are several single-domain antibodies (sdAb), or called heavy-chain variable (VHH) approved or under clinical and pre-clinical research, like Anti-vWF VHH, Anti-HER2 VHH, Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 VHH, Anti-CD8 VHH, Anti-MMR/CD206 VHH and Anti-EGFR VHH for the following uses:
Diagnosis
- Nanobody Immunoassay Format: Lateral Flow Immunoassays and Diagnostic ELISAs
- Biosensors: instantaneous results
- In Vivo Diagnostic Imaging
Therapeutics
- Nanobodies Against Cancer
- Nanobodies Against Autoimmune Diseases
- Nanobodies Against Infectious Diseases
- Nanobodies Against Toxins and Venoms
Yaohai Bio-Pharma Offers One-Stop CDMO Solution for Nano-antibody
Reference:
[1] Hamers-Casterman C, et al. Naturally occurring antibodies devoid of light chains. Nature. 1993 Jun 3;363(6428):446-8. doi: 10.1038/363446a0.
[2] Ingram JR, et al. Exploiting Nanobodies' Singular Traits. Annu Rev Immunol. 2018 Apr 26;36:695-715. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-042617-053327.
[3] Muyldermans S. Nanobodies: natural single-domain antibodies. Annu Rev Biochem. 2013;82:775-97. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-063011-092449.
[4] Jin BK, et al. Nanobodies: A Review of Generation, Diagnostics and Therapeutics. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 22;24(6):5994. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065994.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 SL
SL
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 ET
ET
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 AF
AF
 MS
MS
 BE
BE
 MK
MK
 UR
UR
 BN
BN