DNA Vaccines
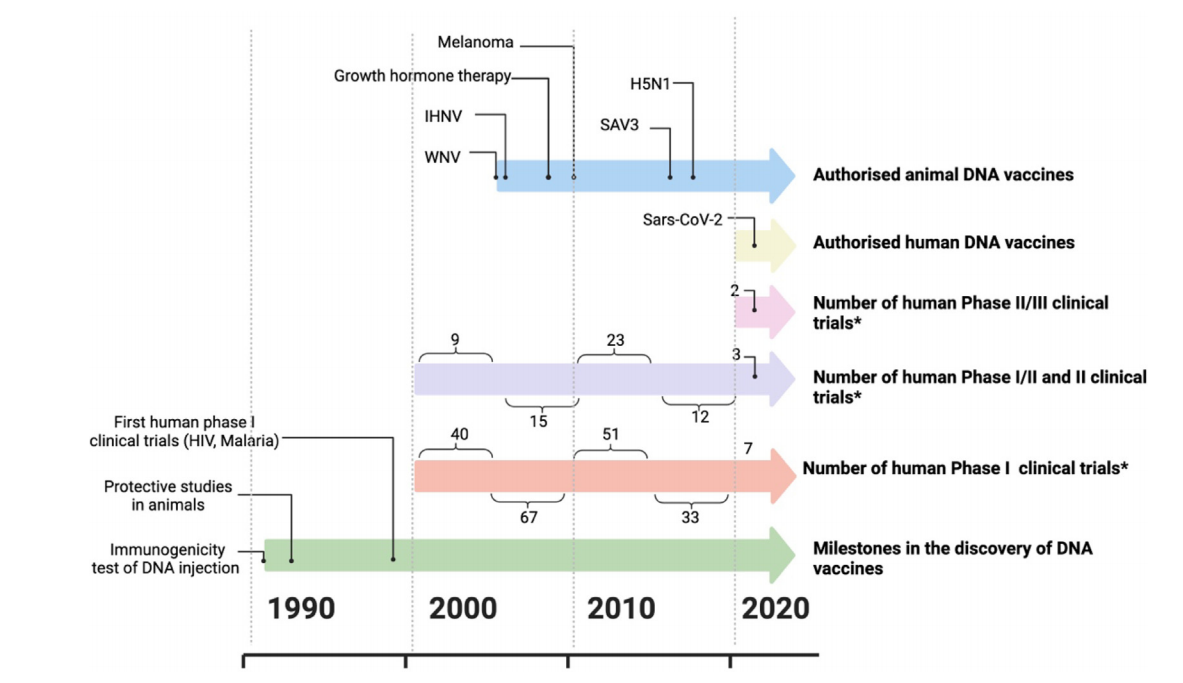
Figure 1. Timeline of DNA Vaccine Development
DNA Vaccines for Animal Use
DNA vaccines in veterinary applications have made great progress as various products have obtained licenses for infectious diseases. To date, DNA vaccines have been successfully approved for preventing H5N1 in chickens (ExactVac), West Nile virus in horses (West Nile-Innovator), infectious haematopoietic necrosis virus in schooled salmons (Apex-IHN), as well as Salmon alphavirus subtype 3 in Atlantic salmon (Clynav).
|
Uses
|
Brand Name
|
Species
|
Target/ Indication
|
Licensed date/ Country
|
Company
|
|
Prophylactic vaccine
|
West Nile-Innovator
|
Horses
|
West Nile Virus (WNV)
|
2005/USA
|
USA CDC, Fort Dodge Animal Health
|
|
Apex-IHN
|
Salmon
|
Infectious haematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV)
|
2005/Canada
|
Novartis Animal Health, Elanco
|
|
Clynav
|
Salmon
|
Salmon alphavirus subtype 3 (SAV3)
|
2016/EU
|
Elanco
|
|
ExactVac
|
Poultry
|
Avian Influenza A (H5N1)
|
2017/USA
|
Huvepharma
|
DNA Vaccines for Human Use
The low immunogenicity in humans still poses a big challenge to DNA vaccine application despite the progress in animal models. Furthermore, the exploration of DNA vaccines for infectious diseases, such as human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV), tuberculosis, and malaria, has prompted the development of diverse optimization strategies in subsequent years.
ZyCoV-D, developed by Zydus Cadila, was the first approved DNA vaccine against SARS-COV-2.
|
Uses
|
Brand Name
|
Target/Indication
|
Stage
|
Company
|
|
Prophylactic vaccine
|
ZyCoV-D
|
Spike-protein; SARS-CoV-2
|
Emergency Use Authorization in India
|
Zydus Cadila
|
Yaohai Bio-Pharma Offers One-Stop CDMO Solution for DNA Vaccine
Reference:
[1] Pagliari S, Dema B, Sanchez-Martinez A, Montalvo Zurbia-Flores G, Rollier CS. DNA Vaccines: History, Molecular Mechanisms and Future Perspectives. J Mol Biol. 2023 Dec 1;435(23):168297. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2023.168297.
[2] Kutzler, M., Weiner, D. DNA vaccines: ready for prime time?. Nat Rev Genet 9, 776–788 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2432.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 SL
SL
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 ET
ET
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 AF
AF
 MS
MS
 BE
BE
 MK
MK
 UR
UR
 BN
BN