According to the central dogma, messenger RNA (mRNA) is the bridge for the transmission of genetic material from DNA to proteins.
mRNA plays a biological role by encoding proteins in vivo, and mature mRNA in eukaryotic organisms consists of five components: 5' Cap (cap structure), 5' UTR (non-coding region), the ORF (open reading frame), 3ʹ UTR, and 3' polyA tail (polyadenylate tail).
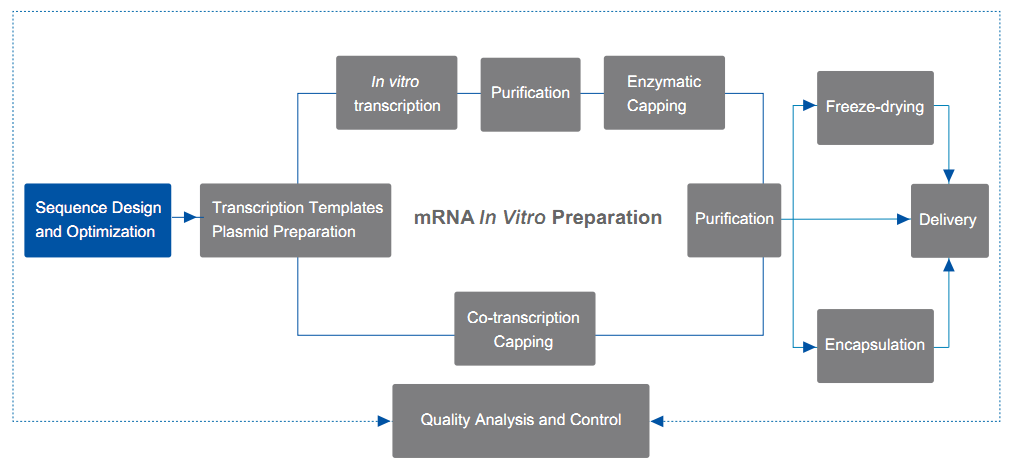
Services Details
| Process |
Optional Service |
Service Details |
Delivery Period (Day) |
| mRNA sequence design and optimization |
Design and optimization of coding sequences |
CDS sequence alignment
CDS codon optimization
|
1 |
| Design and optimization of non-coding sequences |
5' UTR sequence design and optimization
3' UTR sequence design and optimization
polyA sequence design and optimization
|
1-2 |
Customizable Options
| 5’ UTR/3’ UTR |
- Nature UTR sequence
- Mutant/Engineered UTR sequence
|
| 3' PolyA Tail |
- 100A ~120A Tail (recommended)
- Segmented polyA tail
- Other Custom tail
|
Common Strategies for mRNA Sequence Design
| mRNA Components |
Biological Functions |
Optimization Strategies |
| 5’ Cap |
Protect mRNA from degradation by exonucleases and act in concert with the polyA tail at the 3' end, polyA binding protein and translation initiation factor protein to initiate protein translation. |
The natural Cap1 structure avoids pattern recognition receptors and thus reduces the natural immune response, which can be achieved by one-step co-transcriptional capping or two-step enzymatic capping [see mRNA enzymatic capping and co-transcriptional capping for details]. |
| 5’ UTR |
The 5' UTR can be recognized by ribosomes, regulate the translation of mRNA and affect the stability of mRNA. |
Contain Kozak sequences without a very stable secondary structure. Natural UTRs of highly expressed genes are preferred for in vitro transcription (IVT) mRNAs such as α-globin and β-globin. |
| CDS |
Protein-coding regions and coding sequences for antigens, antibodies, or other functional proteins. |
Codon optimization increases the level of translation, noting that certain non-optimal codons may play a role in protein folding. |
| 3’ UTR |
Regulate mRNA translation and stability. |
Natural UTRs of highly expressed genes are preferred for IVT mRNAs such as α-globin and β- globin. |
| 3’ polyA tail |
Regulate protein expression and protect cap structure from degradation. |
Adequate length (100-150 bp) is required; encoding polyA tail on the transcription template plasmid ensures a more defined polyA tail length. |
Our Features
- Diversified UTR source selection
Multiple sources of highly expressed natural & modified UTR libraries; mature UTR modification strategy;
- Cutting-edge CDS optimization team
Cooperate with a professional AI algorithm team to complete the optimization of codons.
- Even polyA tail distribution
Add polyA sequences according to DNA templates to control mRNA length more precisely.
- Diversified optimization combinations
Achieve efficient expression of mRNA with low immunogenicity.
Case study
Sequence Design of a Dual-reporter mRNA: mCherry-eGFP mRNA
Yaohai Bio-Pharma’s mRNA service continues to be upgraded with the design and optimization of a double reporter gene tandem sequence, which achieves co-expression of dual genes.
Using a conventional transfection reagent, the double gene tandem sequence mCherry-eGFP mRNA is transfected into 293T cells, and two fluorescent signals of mCherry (red) and enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) are detected with simultaneous expression after 48 hours, and the stacked graph is highlighted in yellow.

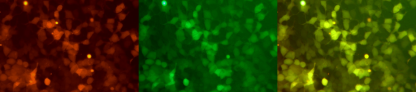
Expression of mCherry-eGFP mRNA in 293T cell

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 SL
SL
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 ET
ET
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 AF
AF
 MS
MS
 BE
BE
 MK
MK
 UR
UR
 BN
BN