5'-end capping is an essential modification of mRNA. mRNAs with cap structures, especially Cap1 structures, facilitate mRNAs evade innate immune responses in vivo, resulting in efficient protein translation.
Enzymatic capping (the two-step method) is the conventional method of mRNA capping, similar to the capping process in eukaryotic organisms. Under the action of a series of enzymes, 7-methylguanine (m7G) is linked to the 5'-end of mRNA through a 5'-5' triphosphate bond and undergoes methylation modification to form the cap structure Cap 1 (m7GpppN).
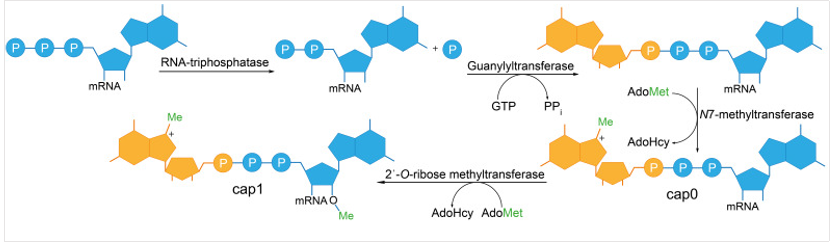
Diagram of natural cap structure formation
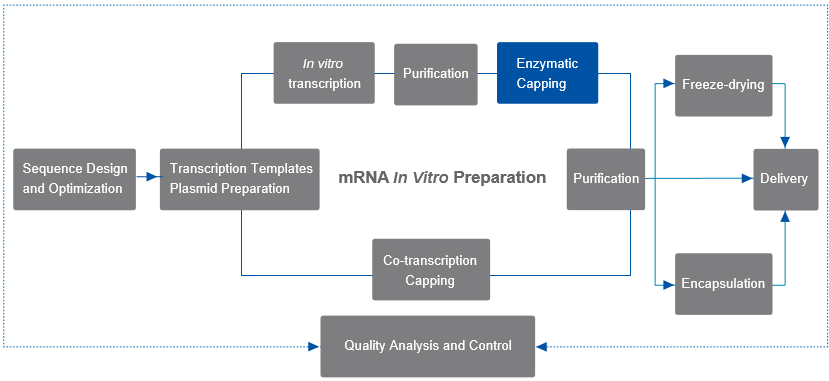
The enzymatic capping reaction flow is as follows:
Linearized plasmid DNA is used as a template for in vitro transcription (IVT) in the presence of T7 polymerase, and mRNA with a 5' end-cap structure is formed after a one-step purification using the vaccinia capping enzyme and 2'-O-methyltransferase.
Services Details
Optional Service |
Service Details |
Delivery Period (Day) |
mRNA enzymatic capping |
Enzymatic capping reaction |
1 |
Capping reaction optimization - optional |
Reaction component design and optimization |
3~7 |
Our Features
- Design and optimization of the capping reaction component
The capping reaction component is optimized, and the production of mRNA transcript is greatly increased.
- In vitro expression verification
The capped mRNA is transfected into 293T cells, and the expression of the target protein can be detected.
- Stringent control of RNase
Through stringent control of the RNaseson experimental environment and consumables, mRNA degradation is effectively prevented.
Case study
Yaohai Bio-Pharma’s mRNA platform has built a perfect capping reaction process.
For eGFP mRNA, an mRNA pre-product prepared by enzymatic capping, an eGFP fluorescence signal (green fluorescence) at a high level can be observed after transfecting 293T cells for 24 hours, which is detected by Western Blot (WB), demonstrating that the target protein enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) can be efficiently expressed in vitro.
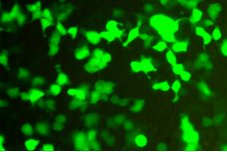

Expression of Enzymatic Capped eGFP mRNA in 293T Cell

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 SL
SL
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 ET
ET
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 AF
AF
 MS
MS
 BE
BE
 MK
MK
 UR
UR
 BN
BN