Regarding the mass production of mRNA, in vitro transcription (IVT) is a more efficient and mature method. The IVT reaction adopts linearized plasmid DNA containing the T7 promoter as a template, and mRNA is synthesized with nucleoside triphosphates (NTPs) as substrates in the presence of T7 RNA polymerase.
Nucleotide modification is a breakthrough in the exploration of mRNA, where unmodified mRNA molecules are recognized by intracellular RNA sensors to activate innate immunity. For considerations of mRNA in vivo immunogenicity and translation efficiency, the IVT process usually employs certain kinds of modified NTPs, and common modified nucleotides are pseudouridine (Ψ), N1-methyl-pseudouridine (N1Ψ), and 5-methylcytosine (5mC).
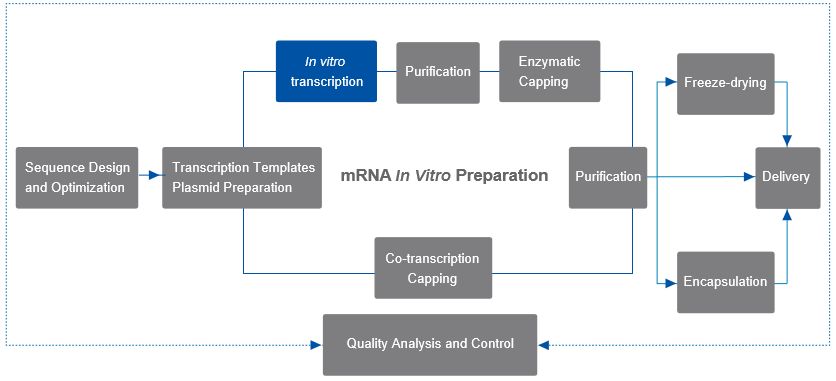
In Vitro Transcription Process of mRNA
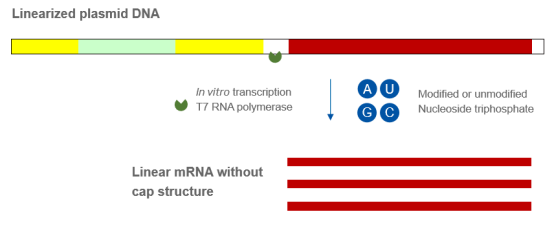
In vitro transcription (IVT) reaction diagram
Services Details
Optional Service |
Service Details |
Delivery Period (Workday) |
In vitro transcription (IVT) |
IVT, In vitro transcription |
1 |
| Nucleotide modifications (Ψ/N1Ψ/5mC, etc.) |
| DNA template removal (DNase I) |
IVT condition optimization - optional |
IVT reaction components design and optimization |
2-5 |
Our Features
- Diversified Nucleotide Modification Strategies
Improve mRNA stability and protein expression in vivo.
- Rigorous Test Design and Optimization
mRNA fragment preparation up to 10kb can be achieved.
By optimizing IVT reaction conditions, the transcription rate is up to 1:200.
- Stringent Control of RNase
Stringent control of RNase through an experimental environment and consumables can effectively prevent mRNA degradation.
Case Study
The current IVT reaction system is roughly optimized for synthetic systems with a length of about 100 nt, not for mRNAs of arbitrary length. The longer the mRNA sequence, the more difficult it is to transcribe and the more prone it is to degradation.
In order to prepare customized mRNA sequences with a length of about 10 kb, Yaohai Bio-Pharma has successfully prepared high-quality samples with a high transcription ratio of 1:135 and obtained 135 μg of initially purified mRNA products after 1 μg of linearized plasmid was transcribed in vitro through rigorous experimental design, continuous optimization of reaction conditions, and strict control of RNase.
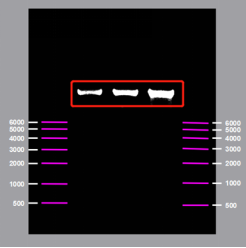
mRNA Identify (Agarose Gel Electrophoresis)

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 SL
SL
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 ET
ET
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 AF
AF
 MS
MS
 BE
BE
 MK
MK
 UR
UR
 BN
BN