Custom saRNA Synthesis
Self-amplifying mRNA (saRNA), also known as replicon RNA, encodes in vitro transcription (IVT) mRNA sequences and viral replicase genes derived from alphavirus or flaviviruses. Viral replicase genes allow the self-amplification of the mRNA, which results in increased protein expression and a minimum required dose of RNA in comparison to non-amplifying mRNAs. Another aspect is that saRNA is a relatively large molecule (more than 14 kb).
Yaohai Bio-Pharma has established a set of mRNA synthesis technologies to provide non-amplifying mRNA and self-amplifying mRNA (1000 nt~14000 nt), such as sequence design and optimization, IVT, purification, lyophilization and lipid nanoparticle (LNP) encapsulation. All products are released under stringent quality control standards.
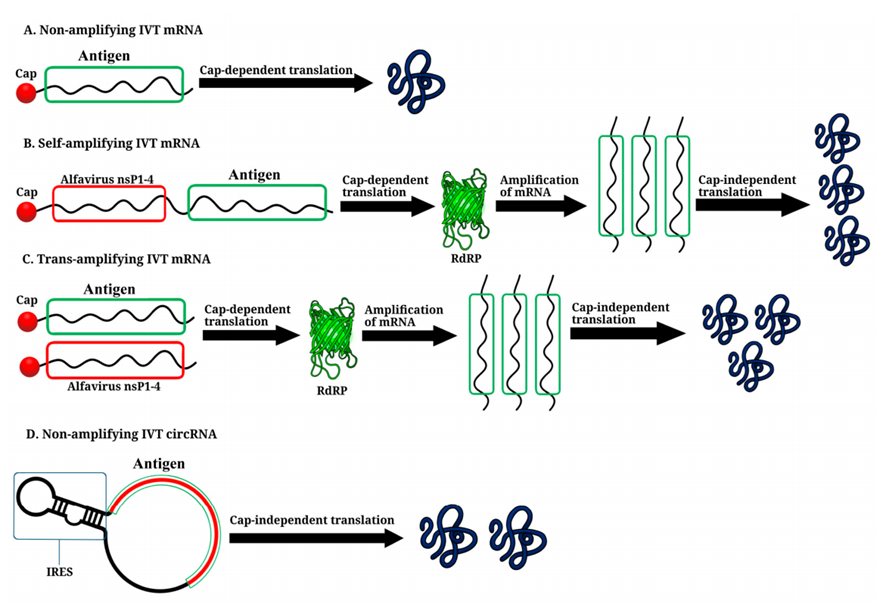
Fig.1 Structural Features of IVT mRNAs: Conventional, Circular and Self-amplifying mRNA.
Sequence Features of Self-amplifying mRNA
The self-amplifying RNA comprises four non-structural proteins (designated as nsP1, nsP2, nsP3, and nsP4), which are derived from alphaviruses, Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus (VEEV). Among these, nsP1 exhibits dual enzymatic activities, namely GTase and N7MTase, whereas nsP2 possesses RTPase activity, pivotal for capping the IVT mRNA to generate Cap 0 structure. Additionally, nsP2 serves as a protease and helicase, facilitating the intricate processing of the entire nsP complex. The precise function of nsP3 remains elusive, yet it engages in interactions with diverse host cell proteins, thereby contributing to the attenuation of the antiviral response mounted by the host.
An alphavirus subgenomic promoter (SGP) region is located before the gene of interest (GOI). The SGP element facilitates the initiation of GOI transcription by bypassing the reading of the sequence encoding viral nsP proteins.

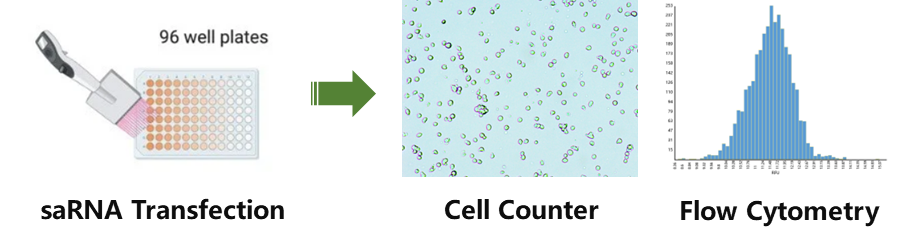
Fig.2 Synthesis and cell assays of eGFP saRNA of Yaohai Bio-Pharma RNASci Platform.
Custom Solutions of saRNA
The synthesis protocol of saRNA is similar to mRNA: Custom mRNA Synthesis
- Sequence Design
- Plasmid Template Preparation
- in vitro transcription (IVT)
- mRNA Enzymatic Capping
- mRNA Co-transcription Capping
- mRNA Purification
- mRNA Lyophilization
- LNP Encapsulation
- Analysis and Testing

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 SL
SL
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 ET
ET
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 AF
AF
 MS
MS
 BE
BE
 MK
MK
 UR
UR
 BN
BN